In the Soviet period, Udmurtiia was given the name Votskaia Autonomous Oblast’ in 1920, and renamed the Udmurt Autonomous Oblast’ in 1932. In 1934, Udmurtiia officially received the status of Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (ASSR), and in 1991, it received the title Udmurt Republic, within the Russian Federation. It is located in the Volga Federal District, and its capital is Izhevsk. Udmurt is an Uralic language also referred to as Votiak and Votyak.
This is a beginning guide to bibliographic tools for researchers of Udmurtiia. Though not a comprehensive overview, this guide outlines two primary ways research can access bibliographic information about Udmurt publications:
(1) The Russian National Library’s Department of Literature in National Languages imprint catalog
(2) The National Library of the Republic of Udmurtiia online library catalog
(3) The letopis’ pechati of Udmurtiia
Additionally, this guide highlights other resources related to Udmurt history, culture, language, and national bibliography.
Researchers may also want to consult the following online database for additional coverage: Elektronnyi katalog knig na iazykakh narodov RF i stran SNG from the Russian National Library. Lastly, this guide highlights the electronic library associated with the National Library of Udmurtiia.
Sources: The Great Soviet Encyclopedia (Volume 25, p. 539); Ethnologue.
LIBRARY CATALOGS
Natsional’naia biblioteka Udmurtskoi Respubliki

The electronic catalogs and databases (Elektronnyie katalogi i bazy dannykh) can be searched in both Russian and Udmurt. On the right hand side users can limit their search by the following categories:
- Elektronnyi katalog: bibliographic records of all holdings received by the National Library of the Udmurt Republic since 1988 (records for documents from before 1988 are in the process of being added).
- Svodnyi kraevedcheskii katalog: Bibliographic records of materials (books, sheet music, maps, legal documents, electronic publications, articles and national and regional periodicals) pertaining to local Udmurt history. These records are either taken from the National Library of Udmurtiia or from municipal public libraries.
- Bibliograficheskaia BD Stat’i: A database of articles (primarily from the social sciences and humanities) published since 2005
- Analiticheskaia BD “Ustoichivoe razvitie sel’skogo khoziaistva: resursy Interneta”: this database holds publications in periodicals and books on matters related to agriculture since 2010
- Analiticheskaia BD “Novye stroitel’nye tekhnologii: resursy Interneta”: database for materials related to economic questions of construction and engineering published since 2010
- Analiticheskaia BD “Dorozhno-transportnyi kompleks: resursy Interneta”: database for materials related to infrastructure and transportation, published since 2010
- Analiticheskaia BD “Energetika. Energopotreblenie i energosberezhenie: resursy Interneta”: database for materials published since 2010 on questions related to the production and management of electric and thermal energy, and the use of alternative forms of energy
On the left hand side users have the option of a basic, advanced or professional search and also have the option to browse by alphabetical listing. In the advanced option users can search by key word, author, title and date of publication, ISSN/ISBN, type of holding, or theme. An image of the advanced search interface is shown below.

Search results give bibliographic information including: The title, author(s), GRNTI, BBK, rubric, available copies and location of copies of the document. An image of the results is shown below.

GENERAL RESOURCES
Publishing in Udmurtiia
The first Udmurt books appeared in the mid-nineteenth century, but in the pre-revolutionary period, Udmurt writers mostly wrote in Russian. In the Soviet period, there was a strong increase in the number of literary works produced in Udmurtiia, due to Udmurt-language education and the foundation of an Udmurt national press and publishing house. The main publishing house in Udmurtiia is Izdatel’stvo Udmurtiia. It was first created in 1922, under the name Idkniga. It published many materials in Udmurt and Russian that were affordable and accessible to the entire population, and literature by major national writers and poets. In 1931, the name of the publishing house changed to Idgiz (Udmurtskoe gosudarstvennoe izdatel’stvo) and in 1961 it became Udmurtiia. It publishes socio-economic works, literature, children’s books, and regional and popular-scientific works. It publishes 50-70 books per year on a wide variety of subjects.
In 1974, 117 books and pamphlets (1,806,000 copies) were published in Udmurtiia. Udmurtiia published 13 periodicals, such as Molot (1921). The following is a list of newspapers published in Udmurtiia and the date at which they began publication: Sovetskoi Udmurtiia (1918), Das’lu (1930), Udmurtskaia pravda (1917), Komsomolets Udmurtii (1921). Users can consult Gazety SSSR 1917-1960: Bibliograficheskii spravochnik 5 for a list of newspapers published in Udmurtiia during these years. On its website, the National Electronic Library of the Udmurt Republic provides access to electronic versions of many of the republican and regional newspapers and periodicals of Udmurtiia for recent years.
Sources: The Great Soviet Encyclopedia (Volume 25, p. 539); Udmurtskaia Respublika. Entsiklopediia (2008), p. 118, 363.
Letopis’ pechati Udmurtskoi Respubliki
Letopisi pechati are chronicles of bibliographic data on all items (within particular categories) published in the Republic of Udmurtiia for a given year. There is detailed bibliographic information provided for each publication. Entry information for these materials includes a general classification number given at the beginning of the section, a consecutive entry number, author, title, place of publication, publisher, date, pagination, illustrations, size, serial statement, ISBN or ISSN, number of copies printed, price, government registration number, e.g. [94-1546]; and other necessary bibliographic information for citations. An example of a letopis’ pechati entry is given in the image below.

It is organized through the use of drop down menus, which allow users to explore the content according to document types: books, dissertation abstracts, art editions, music, reviews, articles, Udmurtia in the Russian press and periodicals (journals and newspapers). Underneath each of these headings there are additional subheadings, which makes browsing very convenient. Note that the files are not downloadable and can only be viewed within the website.
The National Library website makes the letopisi pechati for 2010-2018 available to all users (users can switch to a different year by clicking “arkhiv” at the bottom of the list). Through WorldCat, users can find earlier issues of the letopis’ pechati in physical (OCLC accession number 18425327 or 32150202) and electronic form (OCLC accesion number 609865388 or 728065572).
Archival materials
For users interested in working with archival materials, the website Arkhivy Udmurtii provides helpful resources to navigate the different collections. Most importantly, this website includes:
- A list of republican and municipal archives in the Udmurt Republic
- Lists of archival fonds and opisi for the collections of these archives
- On the pages of specific republican or municipal archives, users can find more detailed descriptions of their collections
- Digital copies of archival materials that are accessible online
- A list of databases that help users search the collections for specific types of materials and subjects
Language and keyboard
Udmurt is an Uralic language also referred to as Votiak and Votyak. Udmurt language uses the Cyrillic script. The Udmurt alphabet includes several characters that do not exist in the Russian alphabet: Ӝ ӝ, Ӟ ӟ, Ӥ ӥ, Ӧ ӧ, and Ӵ ӵ. Users interested in working with vernacular languages can download a Cyrillic extended keyboard that can be used for Udmurt and many of the other national languages of the Russian Federation.
Source: Ethnologue; Udmurtskaia pis’mennost’.
ONLINE RESOURCES
Natsional’naia elektronnaia biblioteka Udmurtskoi Respubliki
The electronic library is a collection of of 24,530 digitized documents. All users have full access to these documents and can access them either by using the search interface or by browsing by particular categories. All documents download as PDF files. With the advanced search option, users can search by keyword, author, title, subject, date issued, and whether or not the item includes a file. The advanced search interface is shown below – note that the interface is in English.
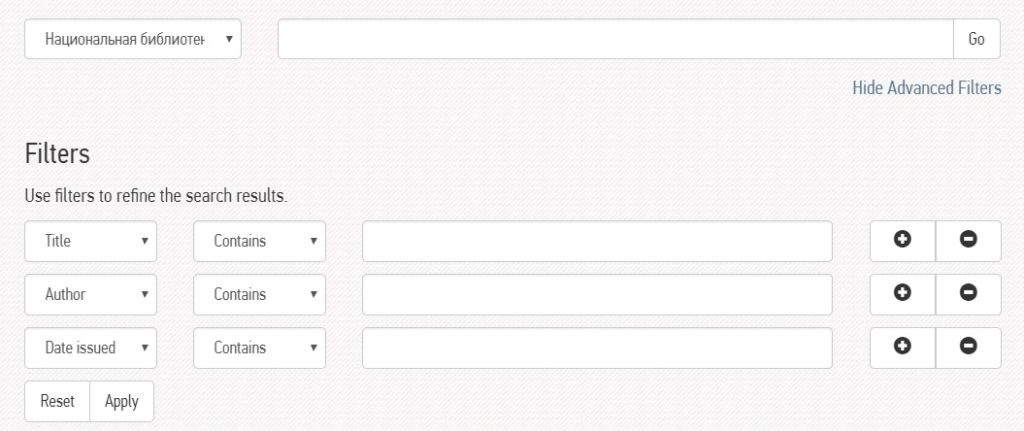
Users can also browse according to themes. The major themes and their sub-themes are listed below.
- National Library of the Republic of Udmurtiia (Natsional’naia biblioteka Udmurtskoi Respubliki)
- History of Udmurtia
- Rare book collection pertaining to Udmurt culture and history from the late 19th century to the early 20th century.
- Udmurt regional periodicals
- Udmurt national periodicals
- Udmurt books
- Udmurt music
- The Udmurt institute of history, language and literature (Udmurtskii institute istorii, iazyka i literatury UrO Ran).
- Rare books
- Institutional publications
- The central municipal library named after Nekrasova and Izhevska (Tsentral’naia munitsipial’naia biblioteka im. N.A. Nekrasova G. Izhevska)
- Materials about Izhevsk
Katalog literatury na udmurtskom yazyke [microform]Rossiĭskai︠a︡ nat︠s︡ionalʹnai︠a︡ biblioteka. Otdel literatury na nat︠s︡ionalʹnykh i︠a︡zykakh.
New York: N. Ross, 1997. U of I Library Call Number: MFICHE 016.94746 R736k5 International and Area Studies Library, Microfilm Room. U of I access. OCLC Accession Number: 702570299
The Russian National Library’s Department of Literature in National Languages [also known as the Department of National Literatures] of the Russian Federation, Commonwealth of Independent States, and the Baltic countries has reproduced holdings catalogs in microfiche format. The national languages imprints catalogs in microfiche format diffuse most of the difficulties associated with transliteration in the vernacular languages, spelling, forms of entry, and uncertainties with the entirety of the collection. Researchers can access the entire holdings for a specific language at the Russian National Library through the microfiche set, conveniently exporting selected titles via PDF scans. The following scans reflect some of the Udmurt language holdings available in microfiche format.



Finno-ugorskie biblioteki Rossii
The online platform Finno-ugorskie biblioteki Rossii is a collaborative project of the National Library of the Karelian Republic, the Russian and East European Institute in Helsinki, the Slavic library of the University of Helsinki, and the M. Kastren Society, is meant to make it easier for users to navigate the different Finno-Ugric libraries in various regions of the Russian Federation and in other countries, and to create an electronic collection of publications in Finno-Ugric languages. Users search by geographical area or by names of important figures in Finno-Ugric literature and folklore. For each of the Finno-Ugric language areas of the Russian Federation – Kareliia, Udmurtiia, Komi, Marii El, Mordoviia, Khanti-Mansiisk, Murmansk, and Tver – the website provides links to major libraries and useful library resources, a list with municipal libraries, and an overview of major educational and research institutions. For resources specifically regarding Udmurtiia, users can follow this link.
The related databases Uralica and Fenno-Ugrika allow users to navigate other digitized Finno-Ugric-language materials. For users interested in more transnational research, the website of the National Library of Komi provides an overview of additional Finn-Ugric resources.